Port Forwards (Port forwarding) feature allows remote computers on the Internet to connect to a specific computer or service within the private LAN.
Different services use different service ports, please verify the service port number before the configuration.
Important:
Make sure the Cudy router gets a Public IP (WAN IP) from your Internet Service Provider, if it’s a Private IP address that means there is another NAT device in front of Cudy. You need to open the service ports on that device as well.
For how to verify the IP Address is a public one or private one, please refer to this link:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network
How to check the WAN IP of Cudy?
Wireless Router & Mesh (System Status->WAN->Status)

4/5 Router (System Status->Cellular/4G->Status)

Note:
1. Usually, if the Public IP and IP Address are the same, it means you've got a Public IP. The IP Address is the WAN IP Address you get from your Internet Service Provider. The Public IP above is the IP Address the other device can find you over internet. So if the Cudy router gets private IP address, you need to figure out which device use this Public IP and open ports on it.
2. For most of the cellular router, the internet service provider usually gives the private IP Address. So, if you want to do the port forwards, please contact your internet service provider to assign you a public IP address or do the port forwarding in their part.
Step 1: Open a web browser and go to http://cudy.net or http://192.168.10.1.
For details, please refer to How to log into the web interface of Cudy Router?
Step 2: Click Advanced Settings -> Port Forwards in the Network section.

Step 3: Click Add to append one entry to the list. Input the parameters as you want into the field as below.
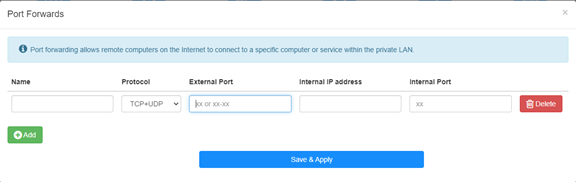
For example: According to the following configure, TCP port 5000, UDP port 5001 and both TCP/UDP port 6000 of host 192.168.10.18 will be opened to the internet.

Name:
Name of the entry, used to facilitate memory
Protocol:
TCP, UDP or TCP+UDP
External Port:
Service port on the WAN side which can be accessed to from the internet
Internal IP address:
IP address of the host, which will open the port to the internet
Internal Port:
Service port of the host in the LAN
Note:
Generally, internal port is the same as the external port.
Step 4: Click 'Save & Apply' to save the settings.
Go to the Status page and check the WAN IP Address of the router. Now you can try to use the http:// WAN IP: port number to visit the service you have opened.

18 comments
@David,
Dear Customer,
Thank you for contacting Cudy support team. Our technical support has contacted you via email. Please check.
Setup Cudy Mesh network.
WR1300 unit is primary and has firmware 2.3.9.
Setup port forwarding.
Setup DDNS with no-ip with address XXX.ddns.net.
Can connect when on Internet.
When on LAN using XXX.ddns.net won’t work. Ports are the same. IP address works.
How do I enable NAT loopback to get it to work?
Setup Cudy Mesh network.
WR1300 unit is primary and has firmware 2.3.9.
Setup port forwarding.
Setup DDNS with no-ip with address XXX.ddns.net.
Can connect when on Internet.
When on LAN using XXX.ddns.net won’t work. Ports are the same. IP address works.
How do I enable NAT loopback to get it to work?
@Ivan,
Dear Customer,
Thank you for contacting Cudy support team.
The NAT loopback function is enabled by default. We don’t list it on the web page.
“Hi Cudy team!
How can I set up “NAT loopback” on the WR3000?
I need this option to access websites hosted on a web server in my home network.”
Hi Cudy team!
How can I set up “NAT loopback” on the WR3000?
I need this option to access websites hosted on a web server in my home network.
Dear Rafal,
PPTP: TCP 1723
L2TP: UDP 1701
IPSec: UDP 500 and 4500
Wireguard: UDP 51820
OpenVPN: TCP or UDP 1194
“Witam,
Proszę napisać które PORTY powinny zostać przekierowane z routera głównego do routera CUDY tak aby prawidłowo działał Server VPN.
Jest kilka rodzajó servera dlatego prosze napisać dokładne Info dla każdego z osobno uwzględniając typ protokołu.
Przykład IpSek → port taki i taki/ UDP/TCP itp …."